Introduction
Urban warfare has become increasingly prevalent in modern times, with over half of the world’s population now living in urban areas. As a result, militaries worldwide are adapting their strategies to incorporate urban warfare tactics. In this blog post, we will explore the rise of urban warfare, its historical context, present-day implications, and examine key urban warfare terminology.
The Rise of Urban Warfare: Historical context and present day implications
Urban warfare has existed throughout history, with ancient armies often attacking cities to gain strategic advantages. However, the significant increase in urbanization over the past century has led to an increase in urban warfare. The trend is expected to continue as urban areas continue to develop and expand. Today, urban warfare poses a significant threat to civilians, as it often results in high levels of collateral damage and casualties.
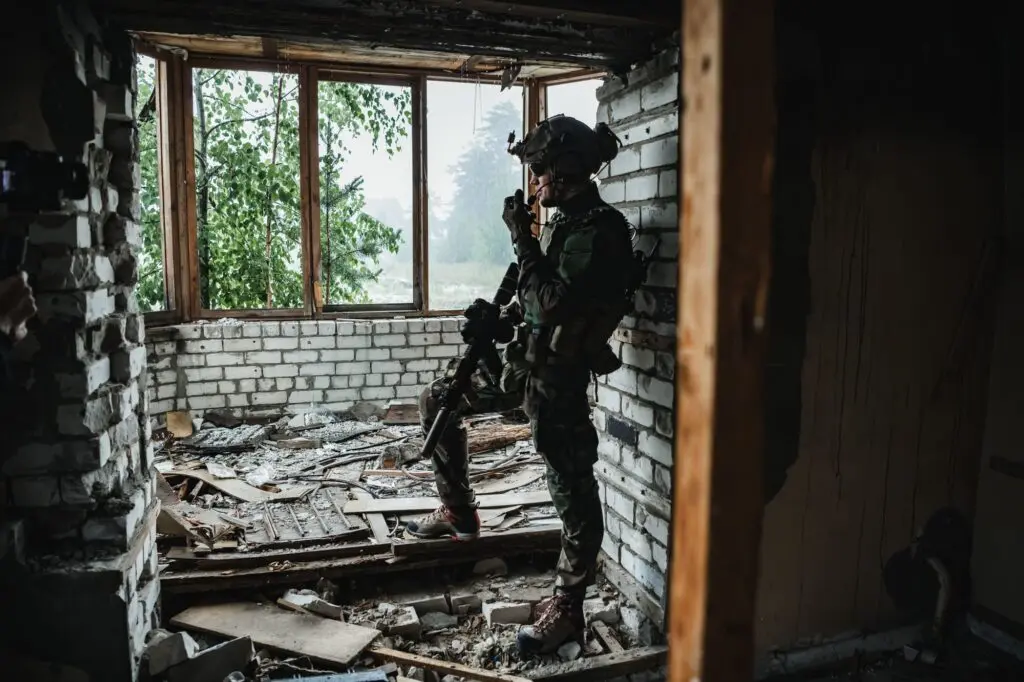

Urban Warfare Terminology
Understanding key terminology related to urban warfare is crucial for both military personnel and civilians. Some common terms that are used in urban warfare include:
- Close Quarters Combat (CQC): Hand-to-hand combat that takes place in confined spaces
- Breaching: The act of entering a building or room
- Rubble Clearing: The removal of debris and rubble from urban environments
- Sniper: A trained marksman who uses long-range rifles to pick off targets from a distance
- IED: Improvised Explosive Device, often used by insurgents in urban warfare
By understanding these terms and others, one can gain a better understanding of the tactics and strategies used in urban warfare environments.
NOAA 2 Way Radios Walkie Talkies 3 Pack - Long Distance Walkie-Talkies with Earpiece and Mic Set Headsets USB Charger Battery Weather Alert
Urban Terrain Analysis
Urban Terrain Characteristics
Urban terrain is a complex environment that poses unique challenges for military operations. The combination of buildings and infrastructure creates a maze of streets, alleys, and hidden areas that can provide cover and concealment for both friendly and enemy forces. Urban environments also tend to restrict line of sight, making it difficult to observe and respond to threats. Understanding the unique terrain characteristics of urban environments is crucial for military personnel to effectively navigate and engage in urban warfare.
Building Structures and Defensive Positioning
Building structures play a critical role in urban warfare, as they can be used for both offensive and defensive purposes. Buildings provide cover and concealment for troops and can be used to establish defensive positions. Understanding the layout of buildings in an urban environment is important to identify potential ambush sites, chokepoints, and other tactical advantages. Defensive positioning in urban warfare requires a combination of protective barriers, such as sandbags and barbed wire, and the use of overlapping fields of fire to provide effective coverage against enemy attacks.

Urban Combat Strategy
Adapting your strategy to the Urban Environment
Military operations in urban terrain present unique challenges that require specific strategies to overcome them. The characteristics of the environment include a complex network of buildings, narrow streets and alleys, and restricted line of sight. To maximize effectiveness, military personnel must adapt their strategies to the urban environment by understanding the terrain, adjusting the tactics and equipment used, and developing intelligence to identify potential threats.
Close Quarter Combat Tactics
The close confines of urban warfare require specialized tactics that differ from traditional warfare scenarios. Close Quarter Combat (CQC) tactics are designed to minimize friendly and civilian casualties while maximizing the effectiveness of engagements in close quarters. These tactics include the use of stun grenades, flashbangs, and breaching techniques to gain entry into buildings. Additionally, troops must be trained in hand-to-hand combat and the use of non-lethal force to subdue potential threats to avoid collateral damage and civilian casualties.
Urban Warfare Technology
Top Urban Warfare Technologies
Military operations in urban terrain require specialized equipment to overcome the unique challenges presented by the environment. From protective gear to advanced weapons systems, top urban warfare technologies include:
- Body armor with enhanced blast resistance
- Non-lethal munitions, including rubber bullets and pepper spray
- Advanced night vision and thermal imaging technology for improved visibility
- Mobile apps for collecting and sharing real-time intelligence
- Lightweight and durable communications equipment
4K Night Vision Binoculars for Adults, 3'' Large Screen Binoculars can Save Photo and Video with 32GB Memory Card & Rechargeable Lithium Battery
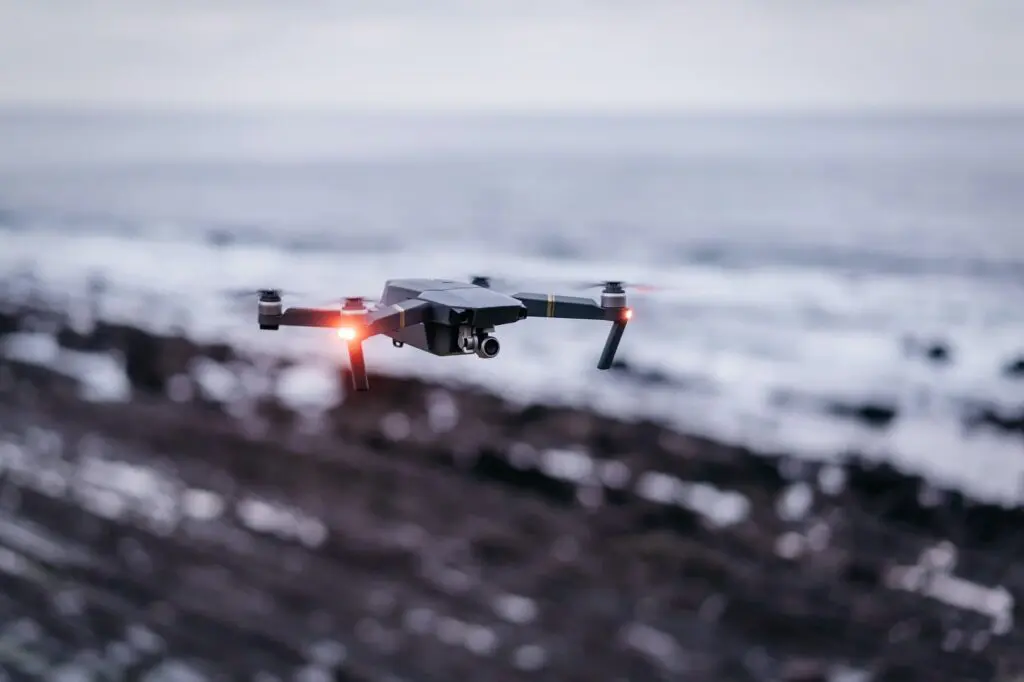
Use of Drones and Robotics
Drones and robotics are increasingly being used in urban warfare to reduce the risks posed to military personnel. Drones equipped with cameras provide valuable real-time surveillance, while armed drones can engage targets without the need for personnel to physically engage. Tactical ground vehicles and robots equipped with sensors and cameras can provide additional surveillance and situational awareness, as well as perform tasks such as neutralizing explosive devices. However, the use of drones and robotics also presents ethical considerations and the risk of collateral damage if not used carefully.

Managing Civilian Presence
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Military operations in urban areas often involve a significant civilian population, which poses unique challenges for managing their presence. Military personnel must abide by international law and ethical standards, including the principles of distinction and proportionality. This means that they must take all possible measures to distinguish between civilians and combatants and avoid targeting civilians unless they are directly participating in hostilities. Furthermore, the use of force must be proportional to the military objective and avoid unnecessary harm to civilians.
Identifying Threats and Distinguishing Civilians from Combatants
Identifying threats and distinguishing between civilians and combatants in urban settings can be difficult. Military personnel must be trained to understand the local culture and language to communicate effectively with the civilian population and gather intelligence. They must also use advanced technologies, such as facial recognition software and biometric data, to identify potential threats and distinguish between civilians and combatants. Training in de-escalation techniques and non-lethal force is also crucial in minimizing harm to civilians and reducing the risk of collateral damage.

Counterinsurgency Operations
Unconventional Warfare Tactics and Strategies
In counterinsurgency operations, military personnel must adapt to unconventional warfare tactics and strategies employed by insurgents, such as the use of improvised explosive devices and guerrilla warfare. To effectively counter these tactics, military personnel must receive specialized training in small-unit tactics and urban combat operations. This includes working closely with local law enforcement agencies and intelligence services to gather information and disrupt insurgent networks.
Surveillance and Intelligence Gathering
Effective surveillance and intelligence gathering are essential components of successful counterinsurgency operations. Military personnel must use a variety of technologies and techniques to gather data on insurgent activities, including human intelligence sources, unmanned aerial vehicles, and signal intercepts. They must also analyze this information to identify patterns and anticipate future attacks. To minimize harm to civilians, intelligence gathering must be conducted in compliance with international law and ethical standards, with measures in place to protect the privacy and rights of individuals.
Urban Warfare Equipment
Recommended Equipment for Urban Warfare
When embarking on urban warfare operations, personnel require specialized equipment to ensure their protection, movement, and survival. Recommended urban warfare equipment includes body armor, helmets, knee and elbow pads, medical kits, first aid supplies, and flashlights.
Choosing the right weapons and gear
When selecting weapons and gear for urban warfare, personnel should consider factors such as mobility, weight, and maneuverability. Recommended weapons and gear include rifles, machine guns, grenades, pistols, and tactical gear. Ultimately, the choice of equipment should be based on the specific needs of the mission and the preference of the personnel using the equipment.

Emergency Response and Medical Care
Effective Medical Care for Urban Combat Injuries
During urban combat operations, military personnel may face injuries that require specialized medical care. To provide effective care, personnel should receive advanced medical training and carry appropriate medical equipment, such as tourniquets, chest seals, and hemostatic agents. They should also be familiar with the best practices for managing injuries in urban environments, such as avoiding contaminated areas and treating wounds quickly to prevent infections.
Handling Casualties and implementing Emergency Procedures
In the event of casualties in an urban warfare situation, emergency procedures must be implemented immediately. Personnel should be trained in triage techniques to prioritize patients based on the severity of their injuries. Medical personnel must also have access to reliable communication channels to coordinate with other teams and hospitals. Additionally, having a well-rehearsed emergency plan can increase the effectiveness of the response and minimize disruptions to the mission.

The Future of Urban Warfare
The future of urban warfare is becoming increasingly complex and challenging. As cities continue to grow and populations become more concentrated, conflicts within urban environments are likely to become more frequent.
One key factor shaping the future of urban warfare is advancements in technology. The use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and robotics is expected to play a significant role in future urban battlefields. These technologies provide a means to gather intelligence, deliver supplies, and engage in combat without risking the lives of soldiers.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also expected to revolutionize urban warfare. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, assisting in decision-making processes on the battlefield. Autonomous weapons systems equipped with AI could potentially increase precision and minimize civilian casualties, although ethical concerns and errors in decision-making algorithms need to be addressed.
Another trend in the future of urban warfare is the blurring of lines between military and civilian populations. In densely populated urban areas, distinguishing between combatants and non-combatants becomes increasingly difficult. This raises questions about the rules of engagement and the protection of civilians.
Urbanization and urban infrastructure will also have significant implications for future urban warfare. Cities are characterized by complex networks of buildings, underground tunnels, and other structures that provide cover and concealment for combatants. The destruction of critical infrastructure, such as communication networks or water supply systems, can cripple cities and have lasting effects on civilian populations.
Additionally, urban warfare in the future is likely to involve an array of actors beyond traditional state-sponsored military forces. Non-state actors like insurgent groups or paramilitary forces could utilize the unique challenges of urban environments to gain strategic advantages over conventional armies.
Overall, the future of urban warfare will require military forces to adapt to dynamic and complex environments. The reliance on advanced technologies and effective strategies that minimize collateral damage and protect civilians will be crucial for success in future urban battlefields.
Maintaining Effective Risk Management and Safety Protocols. Maintaining effective risk management and safety protocols is crucial to ensuring the well-being of individuals and the smooth operation of any organization. By following proper procedures and implementing preventative measures, potential hazards can be identified, controlled, and mitigated to minimize the likelihood of accidents, injuries, or financial losses.
One key aspect of effective risk management is conducting regular risk assessments. This involves identifying potential risks and evaluating their likelihood and potential impact. By systematically assessing the level of risk associated with various tasks, activities, or processes, organizations can prioritize their efforts in implementing appropriate safety measures. This may include revising procedures, providing training to employees, or upgrading equipment to reduce risks.
Another important aspect is establishing clear communication channels for reporting and addressing safety concerns and incidents. This encourages employees to actively participate in the safety culture of the organization by sharing their observations, potential hazards, or near misses. It is crucial to have a reporting system in place that allows all employees to easily communicate their concerns and for the organization to promptly address and mitigate any identified risks.
Additionally, regular safety training and education programs are vital in ensuring that all staff members are aware of potential risks and the necessary safety measures to prevent accidents. These programs should cover a wide range of topics relevant to the organization’s specific industry or environment, such as emergency response procedures, proper use of protective equipment, and the importance of maintaining a clean and organized workspace.
Implementing and regularly reviewing safety protocols and policies is also essential. These should be developed based on industry standards, regulations, and best practices, as well as customized to address the organization’s specific needs and risks. Regular review and updating of protocols ensure that they remain effective and relevant as the organization evolves and new risks emerge.
Lastly, maintaining a culture of safety within the organization is crucial. This involves fostering a mindset where safety is everyone’s responsibility, from top management to front-line employees. Encouraging open communication, providing resources for safety improvements, recognizing and rewarding safety-conscious behavior, and promoting a positive and supportive safety culture are all important in ensuring the continued effectiveness of risk management and safety protocols.
Conclussion
In conclusion, maintaining effective risk management and safety protocols requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular risk assessments, clear communication channels, safety training programs, up-to-date protocols, and a culture of safety. By prioritizing safety and allocating appropriate resources to risk management efforts, organizations can safeguard their employees, assets, and reputation while ensuring a smooth and successful operation.